Your HDA device will be supplied with the latest stable software version already installed. To access the latest features or maintain your system, it is recommended that you perform periodic updates to the OS. This process must be done manually as we do not push updates to systems automatically. Ensure that your system has access to a good internet connection and that power to your HDA device is stable during the process.
In this support article:
If you are not connected to a device
1. Open uControl app
Launch uControl and you will see the home page.
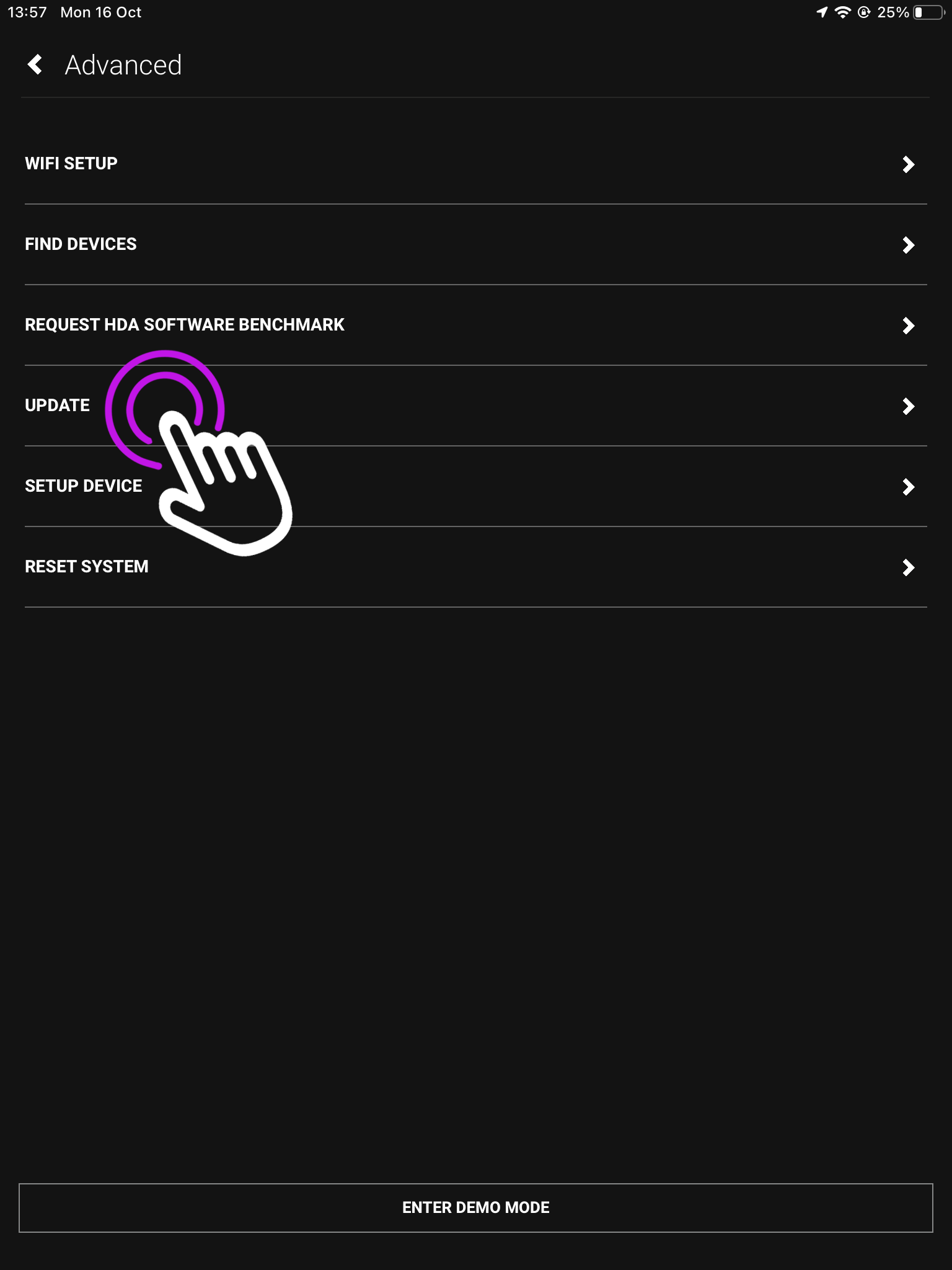
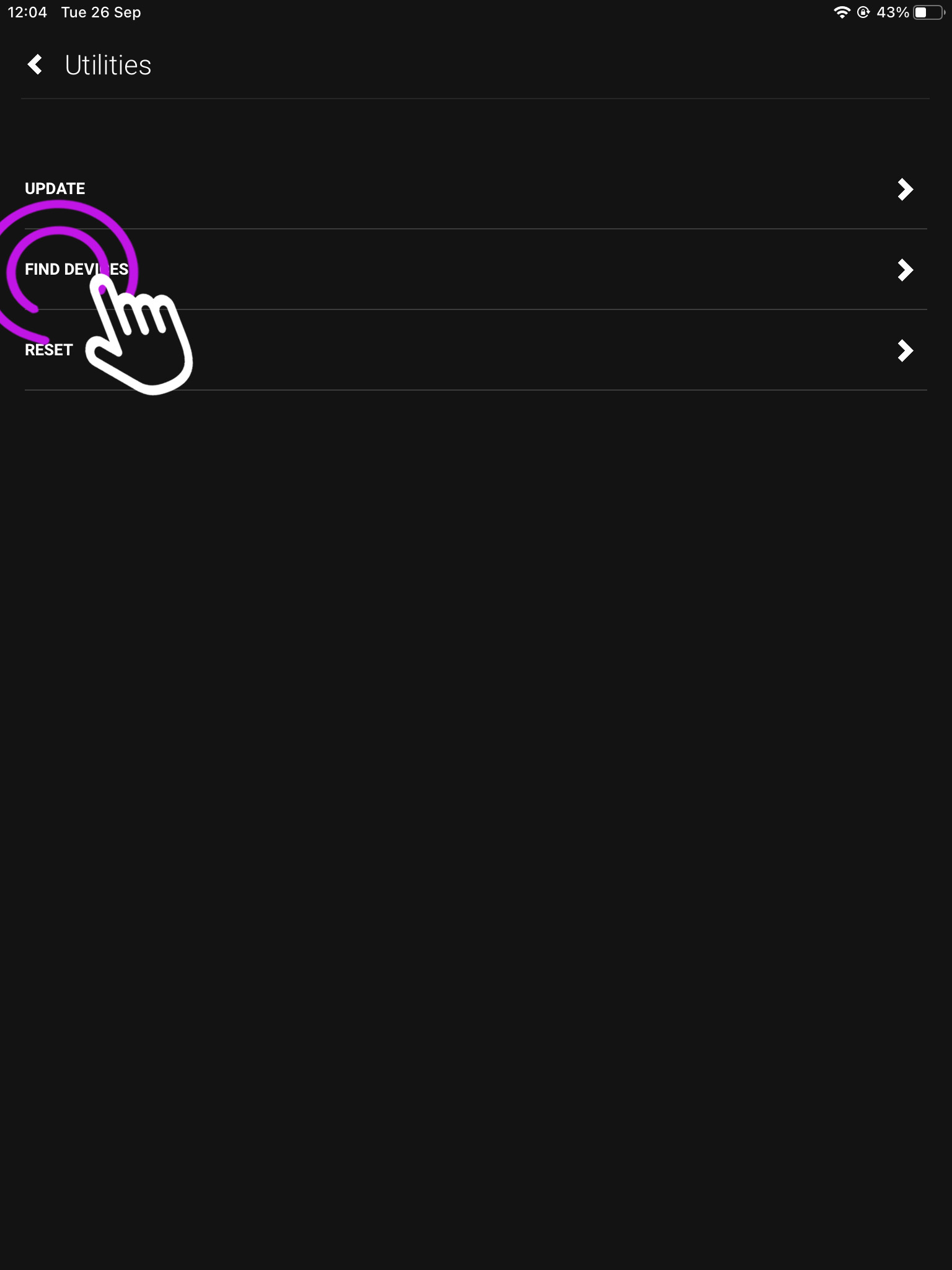
2. Press “Update”
This is the advanced screen where you can find your devices, connect over WiFi, reset your system and more.
3. Enter the devices IP address
If you don’t have this you can get it by finding the IP address of your device.
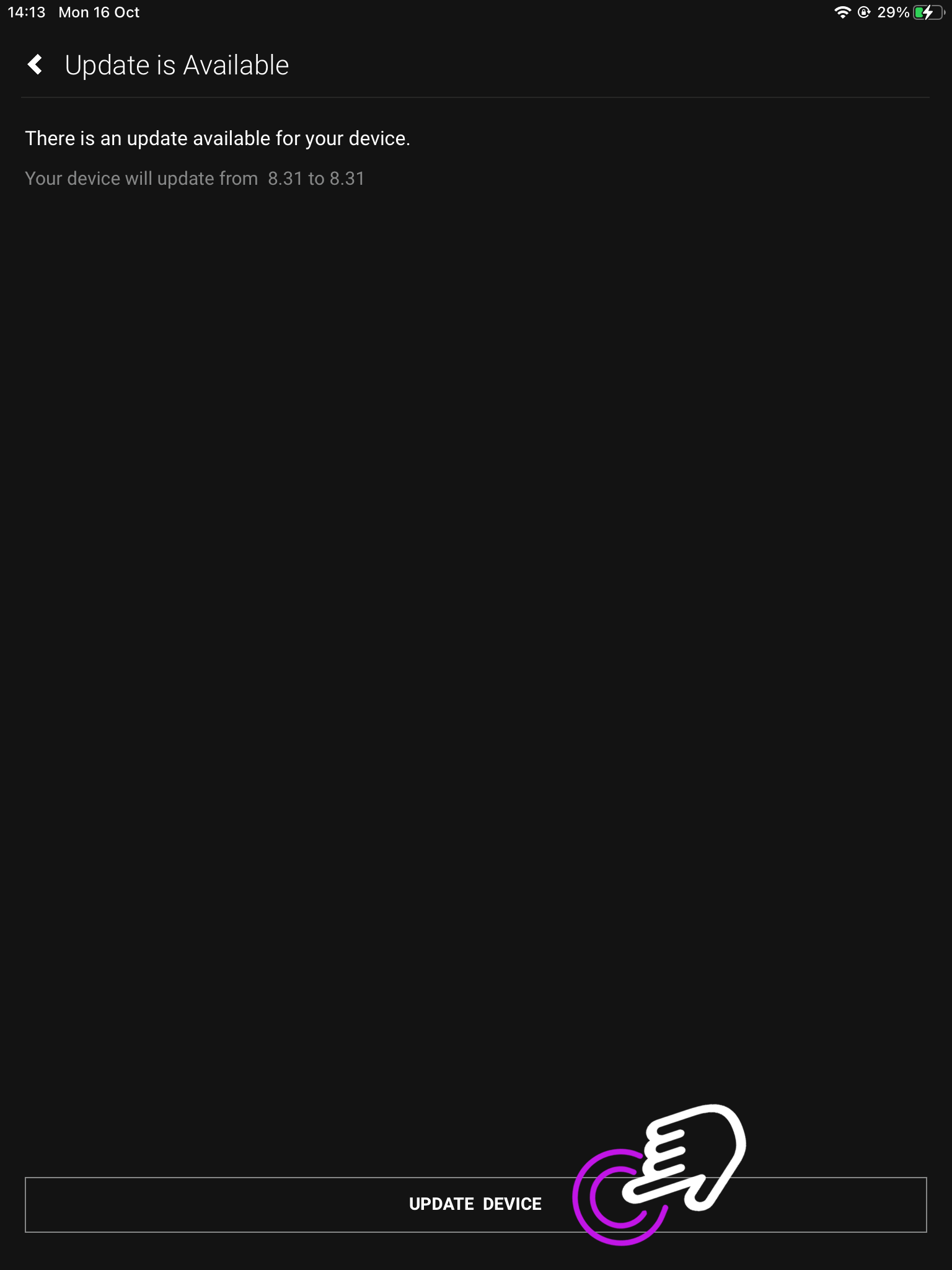
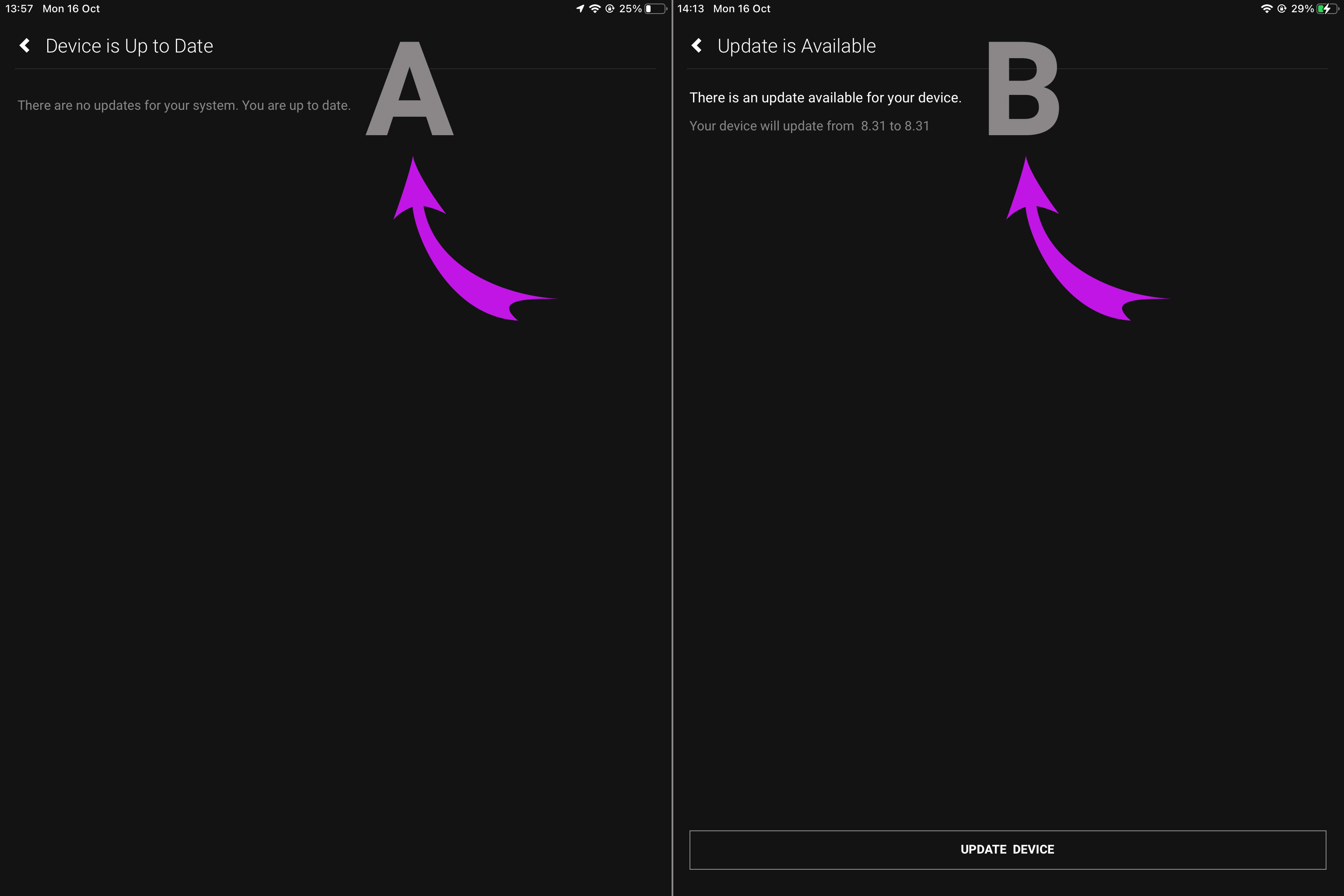
4. Updating your device
A. If there is an available update press “Update Device”.
B. If your device is already up to date, exit this page.
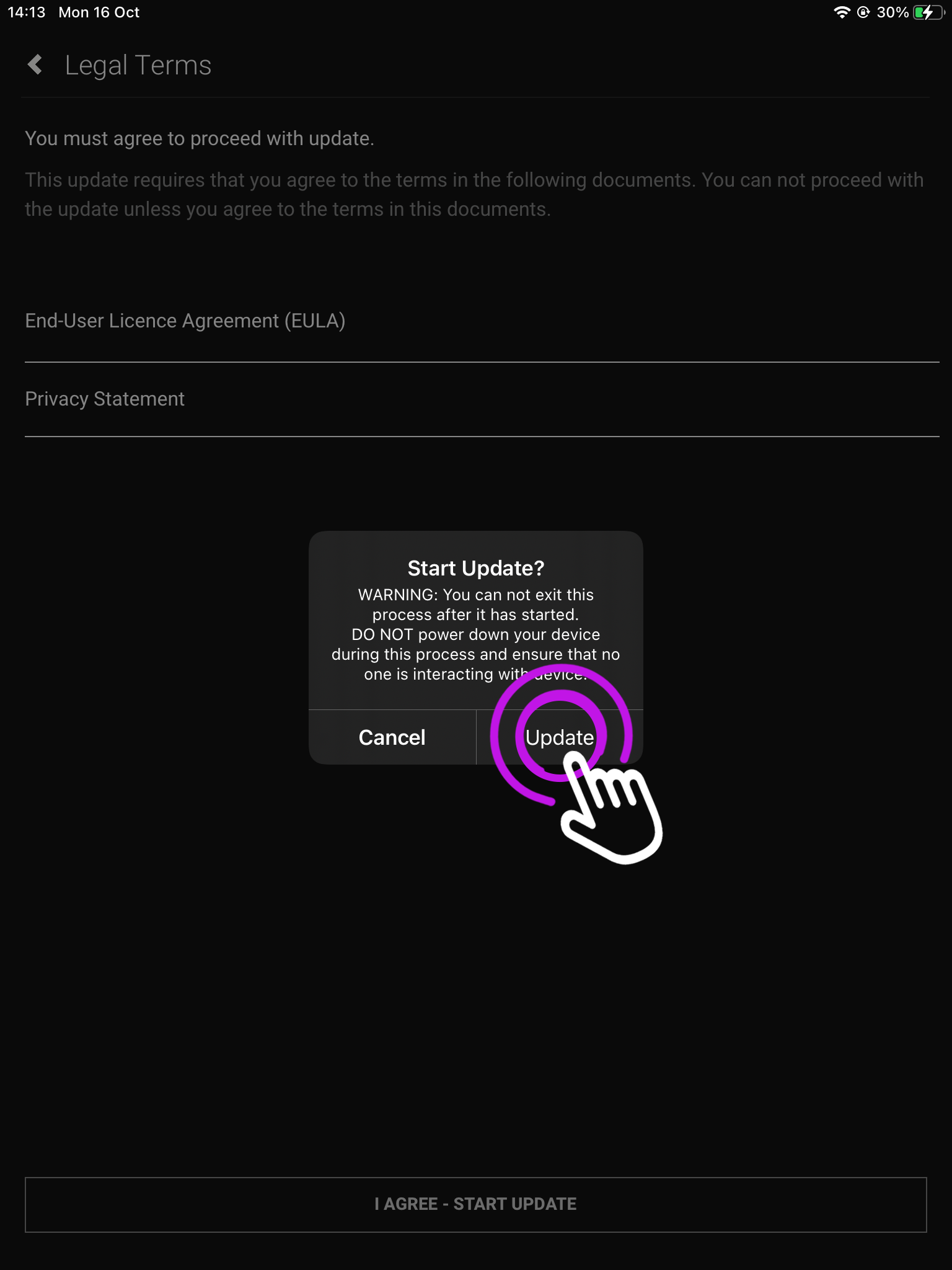
5. Terms and Conditions
To proceed accept the End User Licence Agreement (EULA) and Privacy Statement.
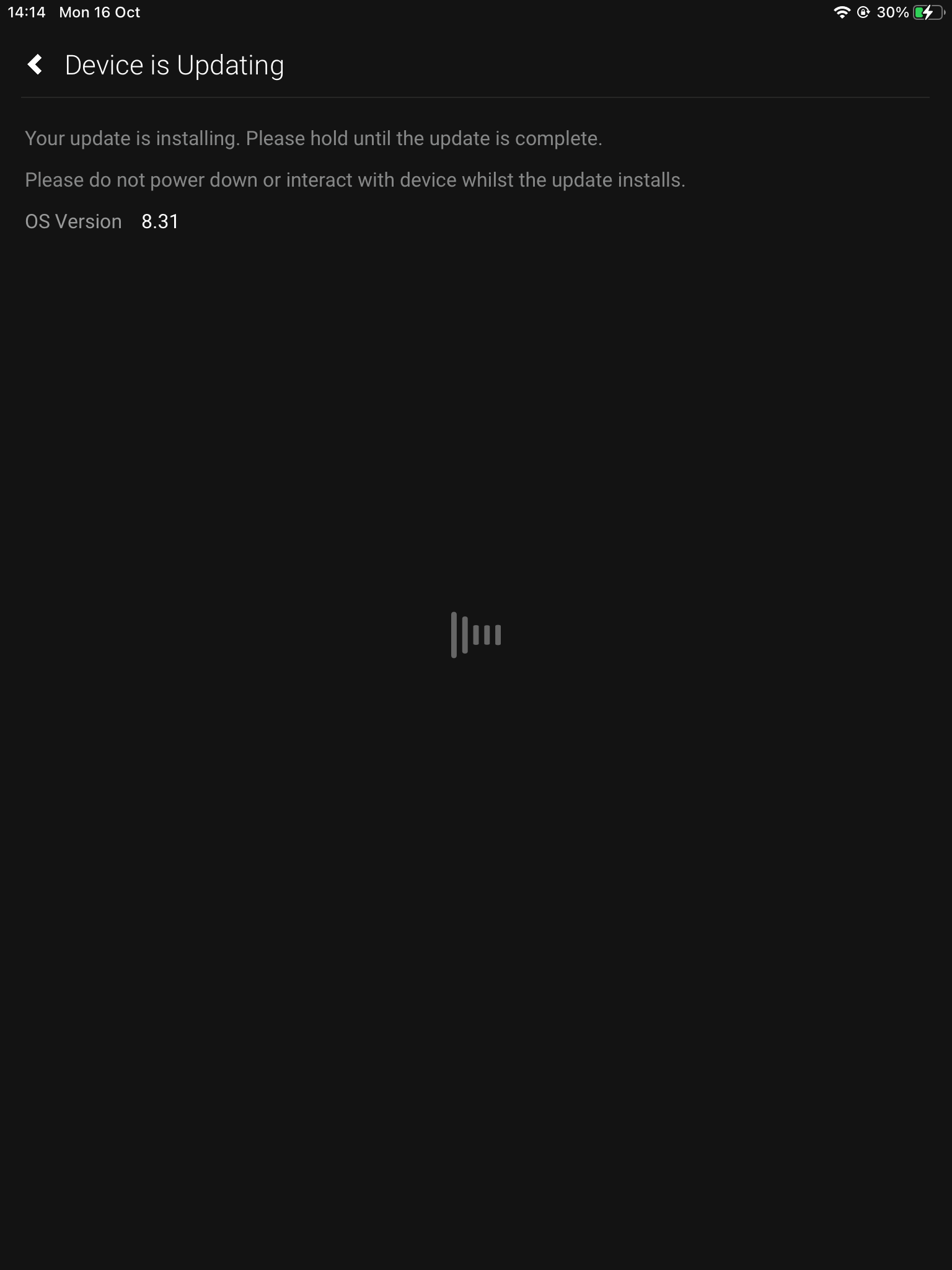
6. Update begins
This process can take up to 5 minutes, however, depending on your network it could be longer.
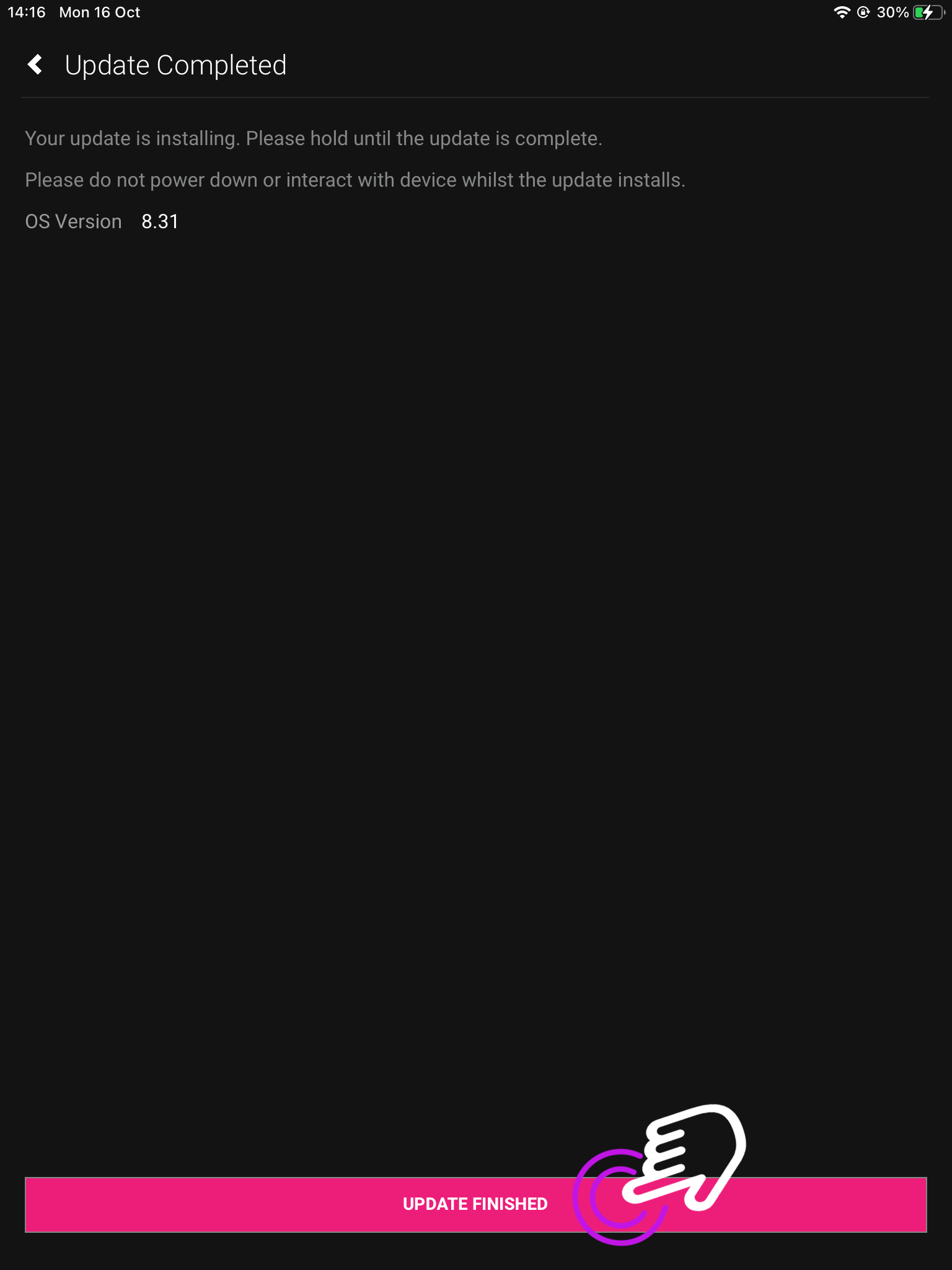
7. Update completed
uControl will display your OS Version.
If you are connected to a device
1. Open up uControl
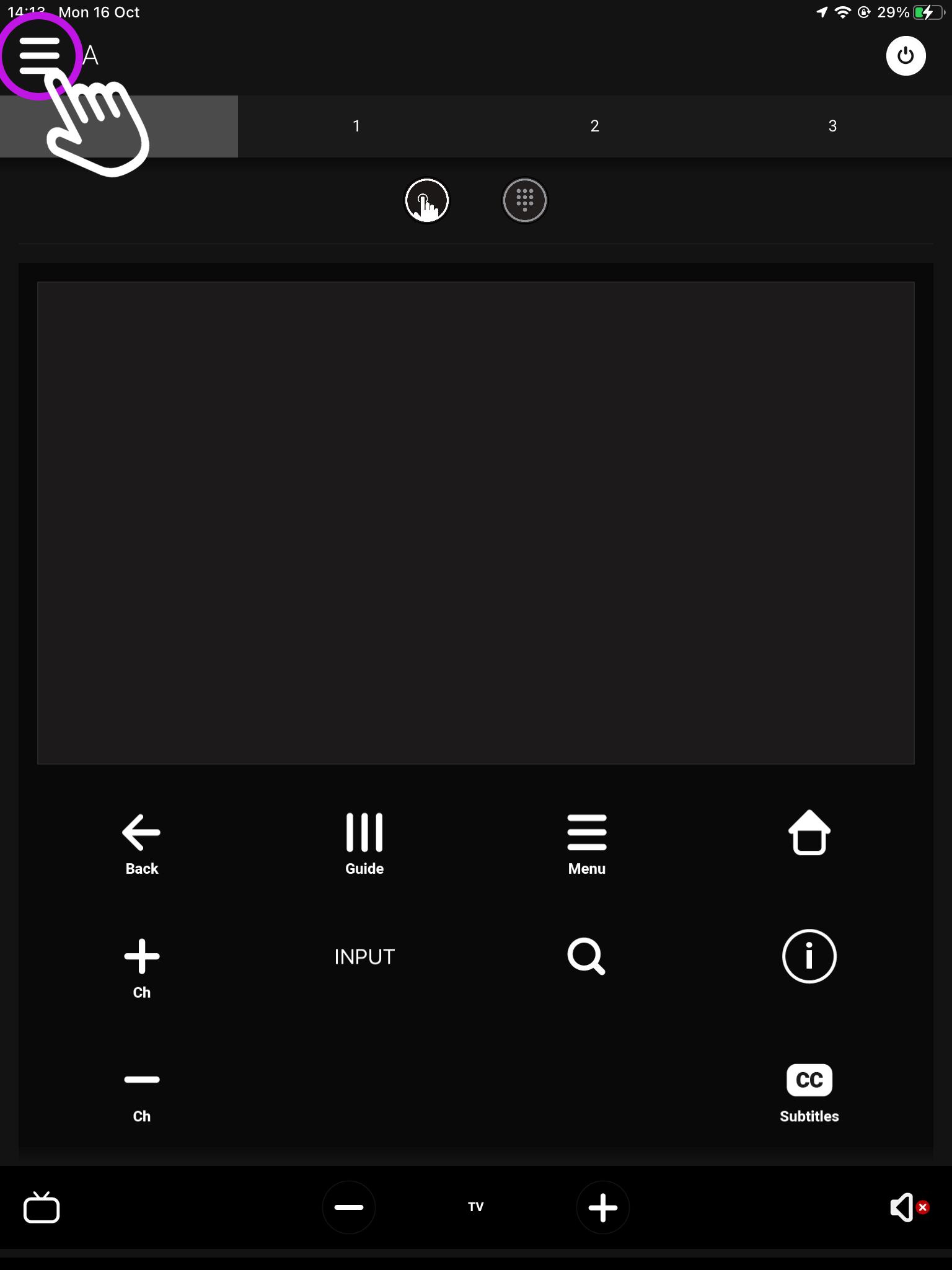
If you’re already connected to a system then you will need to access uControl’s settings. From the main screen you will see something similar to this (see below). From here, look for a menu icon (three horizontal lines) in the top left corner, press that to reveal the Zone selector and Zone control menu.
2. Navigate to your settings
Look for the settings icon located in the bottom left corner.
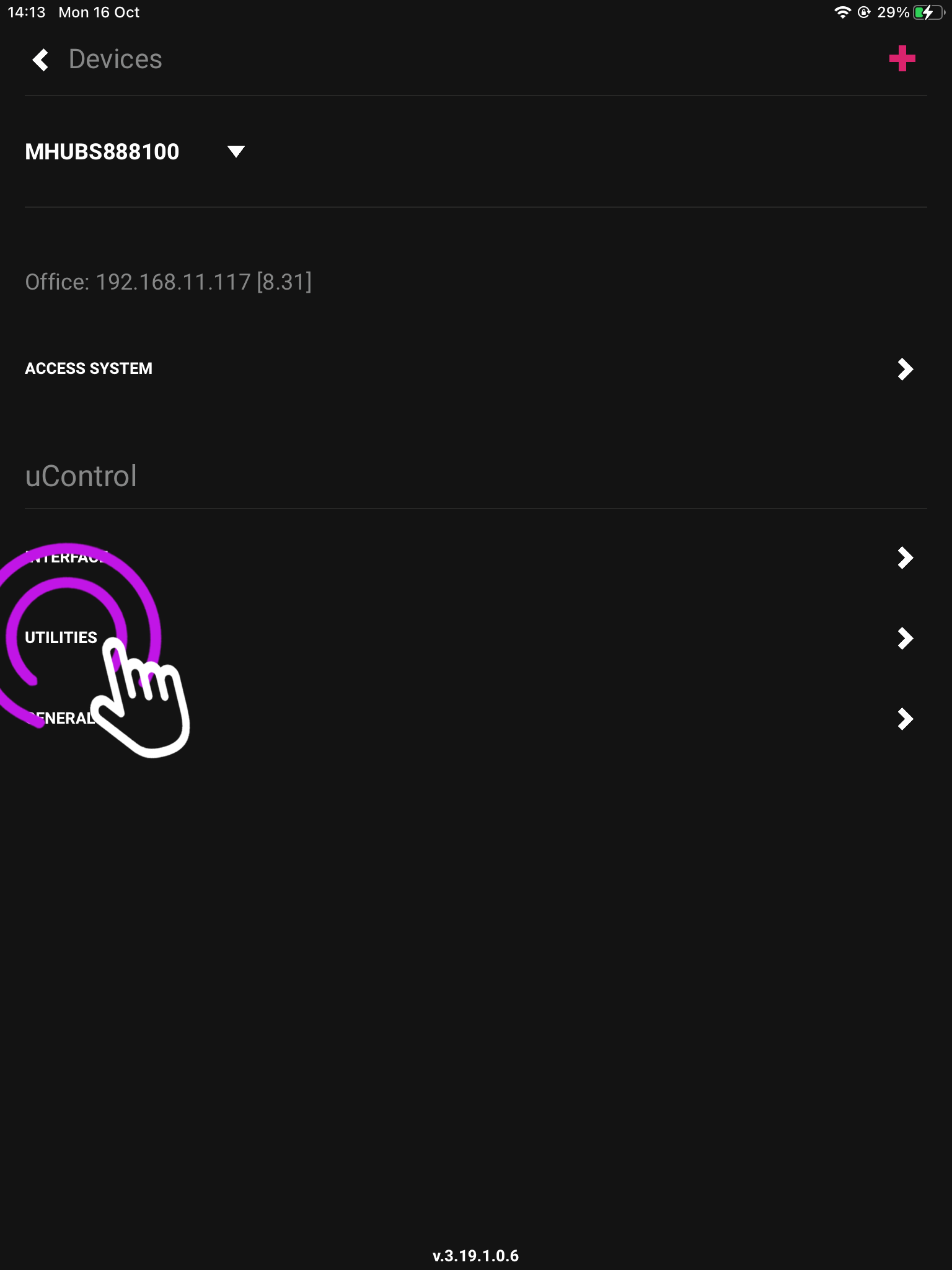
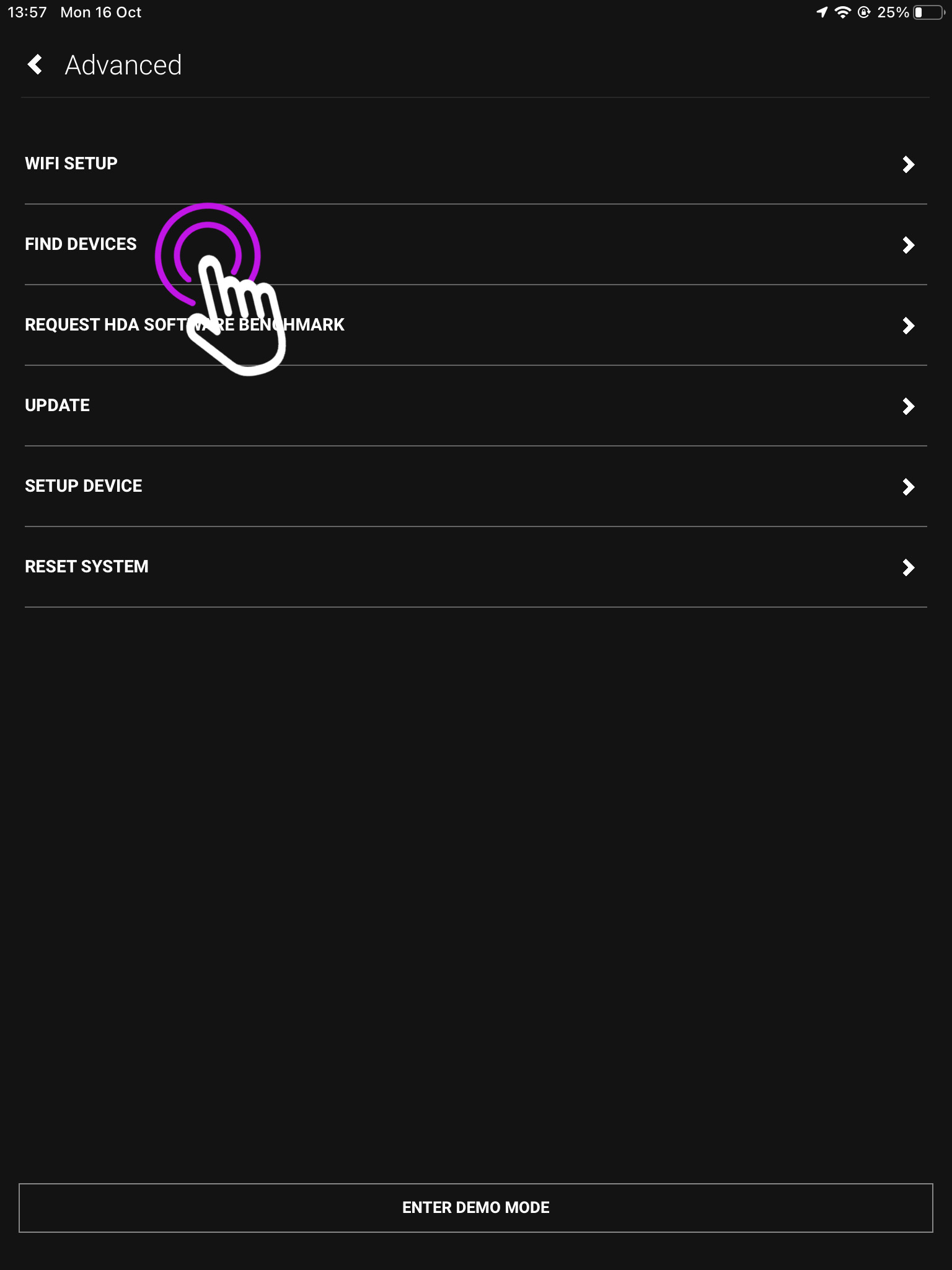
3. Press “Utilities”
This will take you to your devices service page.
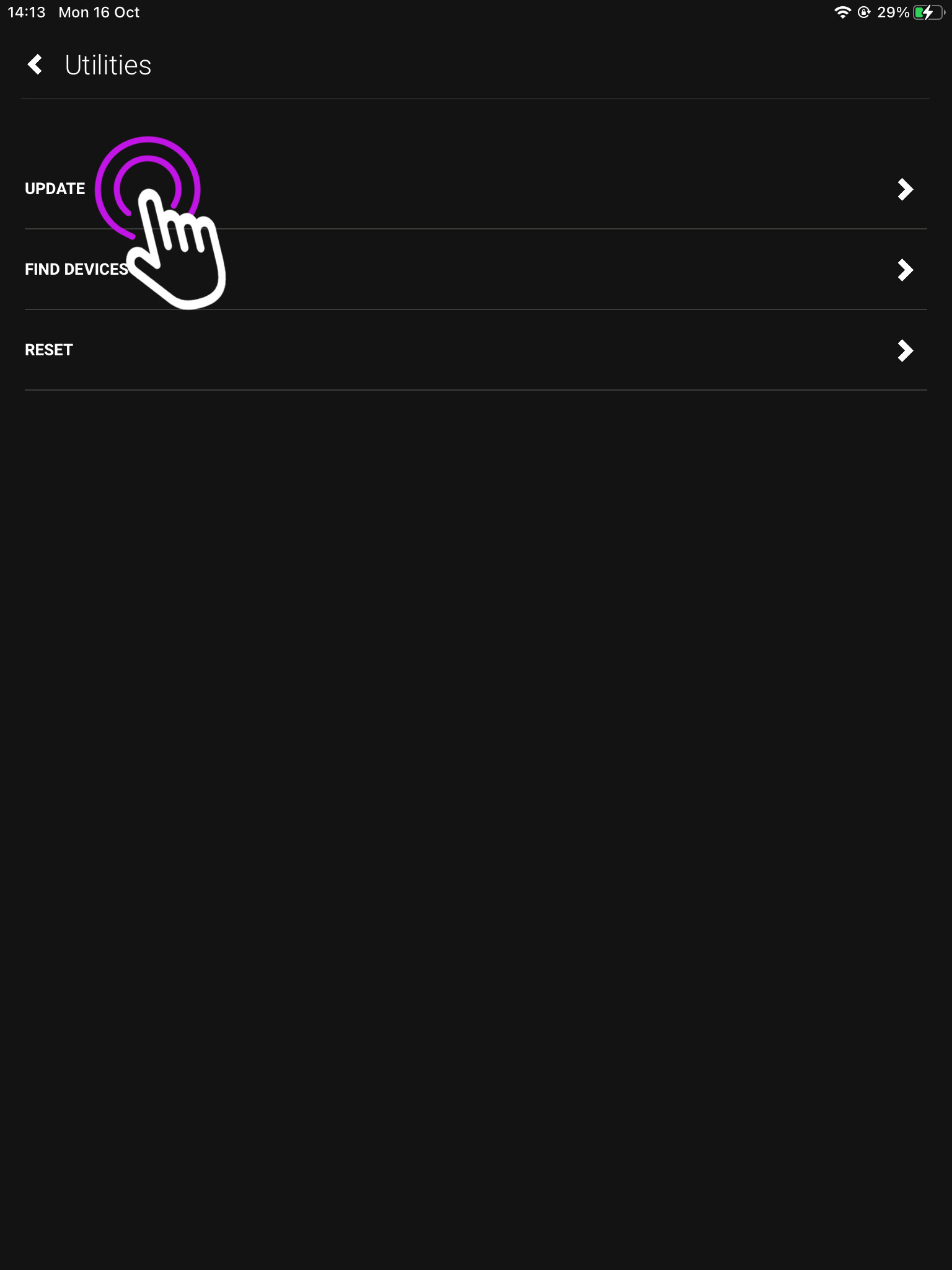
4. Press “Update”
From this page you can also find your devices, and reset one. To find out more check out our uOS Utilities page.
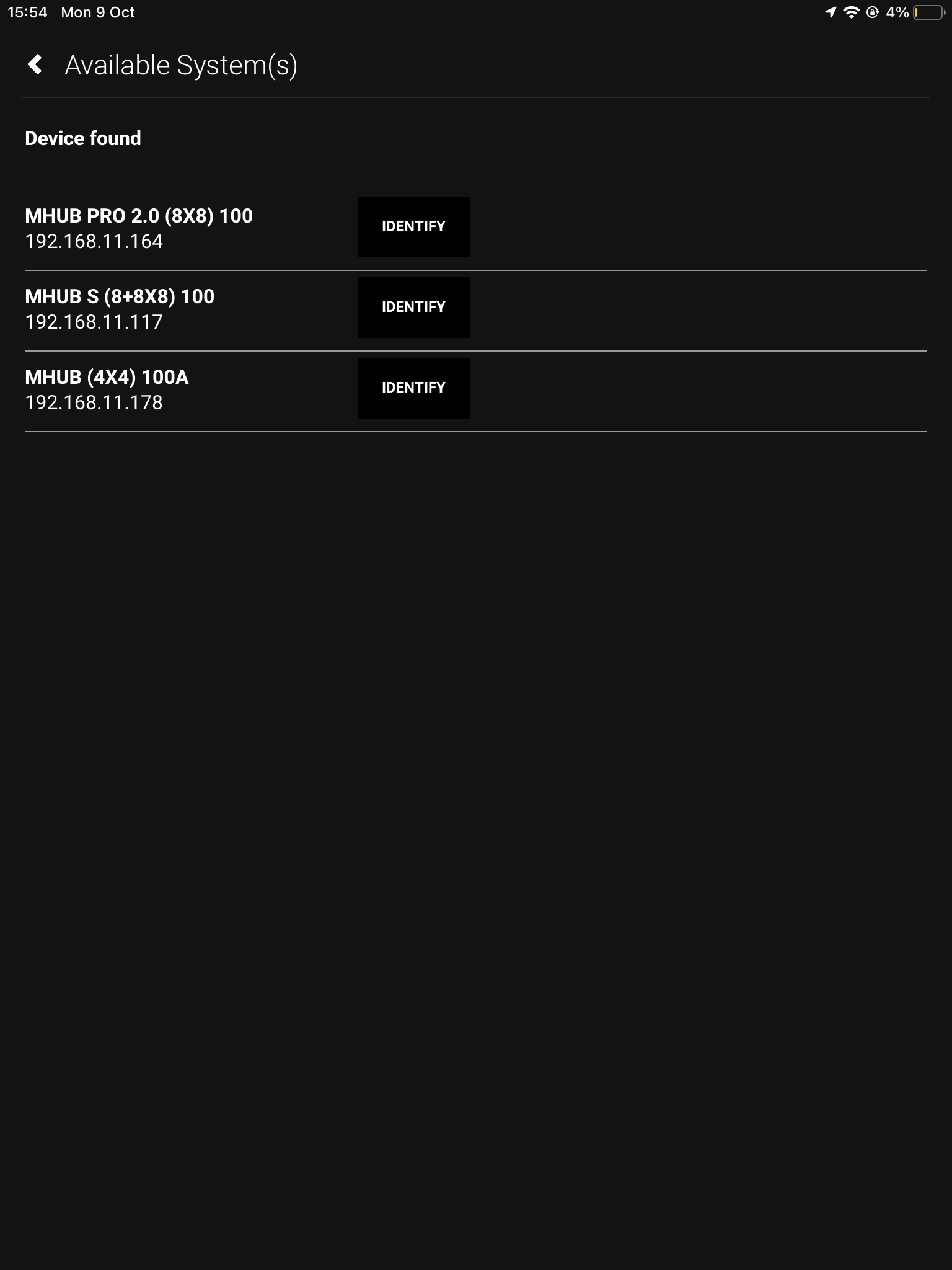
5.“Available Systems”
If you have a stacked system, or multiple devices they will show here.
6. Begin update
If your device is updateable it will start, and include which version you’re updating to.
7. Terms and Conditions
To continue please acknowledge the legal terms.
8. Await download
This process can take up to 5 minutes, however, depending on your network it could be longer.
9. Update completed
uControl will now let you know the update is complete.